1.3.4. Domains & Color
Example files that accompany this section: http://grasshopperprimer.com/appendix/A-2/1_gh-files.html
The color wheel is a model for organizing colors based on their hue. In Grasshopper, colors can be defined by their hue value in a range of 0.0 to 1.0. Domains are used to define a range of all possible values between a set of numbers between a lower limit(A) and an upper limit (B).

In the color wheel, hue corresponds to the angle. Grasshopper has taken this 0-360 domainand remapped it between zero and one.
By dividing the Hue domain (0.0 to 1.0) by the number of segments desired, we can assign a hue value to each segment to create a color wheel.
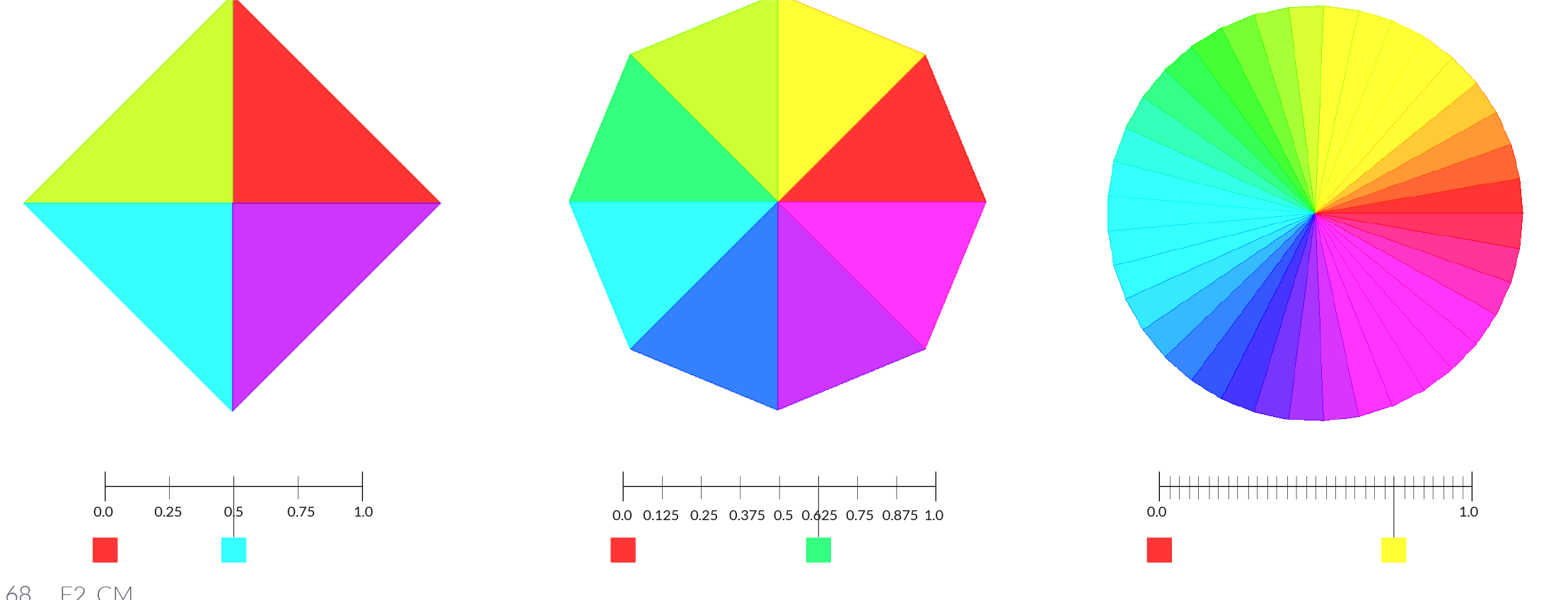
In this example, we will use Grasshopper’s domain and color components to create a color wheel with a variable amount of segments.
|
|
|
| 01. |
Type Ctrl+N (in Grasshopper) to start a new definition |
|
| 02. |
Curve/Primitive/Polygon – Drag and drop a Polygon component onto the canvas |
 |
| 03. |
Params/Geometry/Point – Drag and drop a Point Parameter onto the canvas |
 |
| 04. |
Right-Click on the Point Component and select set one point |
|
| 05. |
Set a point in the model space. |
|
| 06. |
Connect the Point Parameter (Base Point) to the Plane (P) input of the Polygon component |
|
| 07. |
Params/Input/Number Sliders – Drag and drop two Number Sliders onto the canvas |
|
| 08. |
Double-click on the first Number Sliders and set the following:Rounding: Integers
Lower Limit: 0
Upper Limit: 10
Value: 10 |
|
| 09. |
Double-click on the second Number Sliders and set the following:Rounding: Integers
Lower Limit: 0
Upper Limit: 100
Value: 37 |
|
| 10. |
Connect the Number Slider (Radius) to the Radius (R) input of the Polygon component When you connect a number slider to a component in will automatically change its name to the name of input that it is connecting to. |
|
| 11. |
Connect the Number Slider (Segments) to the Segments (S) input of the Polygon component |
|

|
|
|
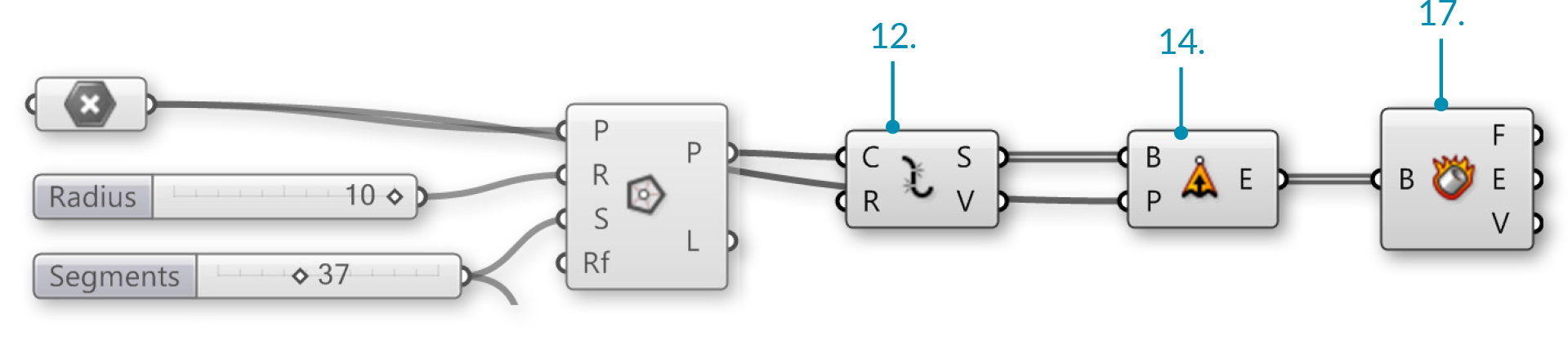
| 12. |
Curve/Util/Explode – Drag and drop an Explode component onto the canvas. |
 |
| 13. |
Connect the Polygon (P) output of the Polygon component to the Curve (C) input of the Explode component |
|
| 14. |
Surface/Freeform/Extrude Point – Drag and drop the Extrude Point component onto the canvas |
 |
| 15. |
Connect the Segments (S) output of the Explode component to the Base (B) input of the Extrude Point |
|
| 16. |
Connect the Point Parameter (Base Point) to the Extrusion Tip (P) of the Extrude Point component |
|
| 17. |
Surface/Analysis/Deconstruct Brep – Drag and drop the Deconstruct Brep component on to the canvas |
 |
| 18. |
Connect the Extrusion (E) output of the Extrude Point component to the Deconstruct Brep (B) component |
|
|
|
|
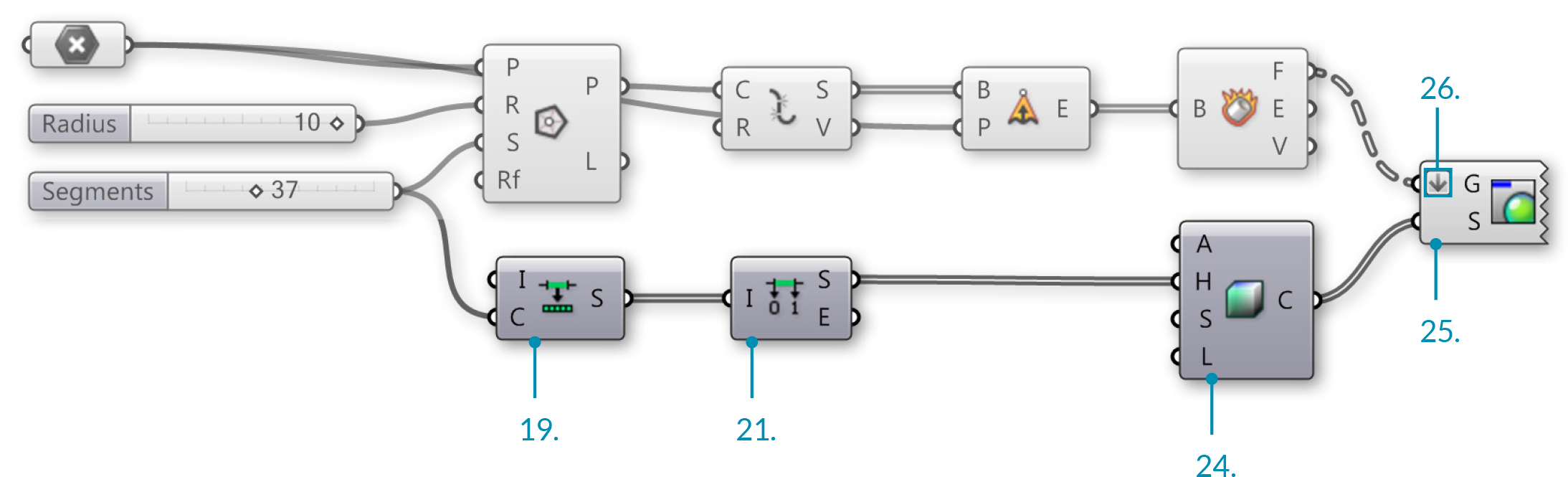
| 19. |
Maths/Domain/Divide Domain – Drag and drop the Divide Domain componentThe Base Domain (I) is automatically set between 0.0-1.0 which is what we need for this exercise |
 |
| 20. |
Connect the Number Slider (Segments) to the Count (C) input of the Divide Domain component |
|
| 21. |
Math/Domain/Deconstruct Domain – Drag and drop the Deconstruct Domain component |
 |
| 22. |
Connect the Segments (S) output of the Divide Domain component to the Domain (I) input of the Deconstruct Domain component |
|
| 23. |
Display/Colour/Colour HSL – Drag and drop the Colour HSL component |
 |
| 24. |
Connect the Start (S) output of the Deconstruct Domain component to the Hue (H) input of the Colour HSL components |
|
| 25. |
Display/Preview/Custom Preview – Drag and drop the Custom Preview component |
 |
| 26. |
Right click on the Geometry (G) input of the Custom Preview component and select FlattenSee 1-4 Designing with Data Trees for details about flattening |
|
| 27. |
Connect the Faces (F) output of the Deconstruct Brep component to the Geometry (G) input of the Custom Preview component |
|
| 28. |
Connect the Colour (C) output of the Colour HSL component to the Shade (S) input of the Custom Preview component |
|
For different color effects, try connecting the Deconstruct Domain component to the saturation (S) or Luminance (L) inputs of the Colour HSL component.


















